WASHINGTON — What got done here this week at the Assn. of National Olympic Committees meeting was not nearly as noteworthy as two other essentials: the fact that the meeting was held in the first place in the United States and that delegates from 204 entities were on hand.
As the session gaveled to order on Thursday, there in their place in the rows of seats were, for instance, representatives from North Korea.
From Syria.
Russia.
Everywhere in the world, including two new national Olympic committees, Kosovo and South Sudan.
There are actually 206 national Olympic committees. The Republic of Congo didn't make it. And elements of the government of Kuwait are involved in a fight with the IOC, meaning the national Olympic committee is now suspended, for the second time in five years, amid political interference; moreover, on Thursday, the IOC announced it had revoked the Olympic qualifying status of a shooting championship in Kuwait, due to begin next week, because an Israeli official was denied a visa for the event.

The assembly marked the first time the ANOC session has been held in the United States since 1994, two years before the Atlanta 1996 Summer Games.
With Los Angeles now bidding for the 2024 Games, the stakes were high here for the U.S. Olympic Committee.
As the familiar saying goes, LA surely could not win anything here -- but a poor performance could cost it and the USOC, even though the 2024 race is still in its early stages.
The International Olympic Committee won’t pick the 2024 winner until September 2017. Five cities have declared for the 2024 race: LA, Paris, Rome, Budapest and Hamburg, Germany.
The tentative verdict: no major missteps. All good.
"No problem with [U.S. entry] visas. It was fantastic," the ANOC general secretary, Gunilla Lindberg of Sweden, said Friday, adding of the assembly and related events, "The organization went really well. I heard only positive comments."
Does that mean LA is on course to a sure victory?
Hardly.
Indeed, by most accounts, Paris is considered the 2024 front-runner.
"Two years is a long time," Paris 2024 chief executive Etienne Thobois said. "It's a long journey ahead. 'Favorite' doesn't mean anything."
The calm here simply mean it's on to whatever the future holds, with both the strengths and the challenges underscoring the American effort here this week on full display.
A clear and undisputed strength: Los Angeles mayor Eric Garcetti.
Garcetti, bid chairman Casey Wasserman and Janet Evans, the 1980s and 1990s Olympic swimming champ, make up the public face of the LA 2024 bid. The Olympic movement in recent years has rarely seen a personality like Garcetti: a mayor who leads from the front and in a style that is both fully American and decidedly international.

Garcetti got to welcome to the United States, among others, Tsunekazu Takeda, the Japanese IOC member and Tokyo 2020 leader who for the past year has also been the IOC’s global marketing commission chair.
Takeda speaks English. But no. Garcetti spoke with him in Japanese. When they parted, the mayor passed to Takeda a business card — in Japanese.
Meeting Julio Maglione, the IOC member from Uruguay who is president of both the international swimming federation, FINA, and PASO, the Pan-American Sports Organization, Garcetti spoke in Spanish.
South Sudan? Garcetti, a Rhodes Scholar some 20 years ago, knows the region; he said he lived in East Africa, studying Eritrean nationalism, in the mid-‘90s.
The mayor’s back story — which surely will become ever more widely known — is, truly, remarkable.
Garcetti served for years on the LA city council before becoming mayor. As LA Times columnist Steve Lopez wrote the week before that 2013 mayoral election:
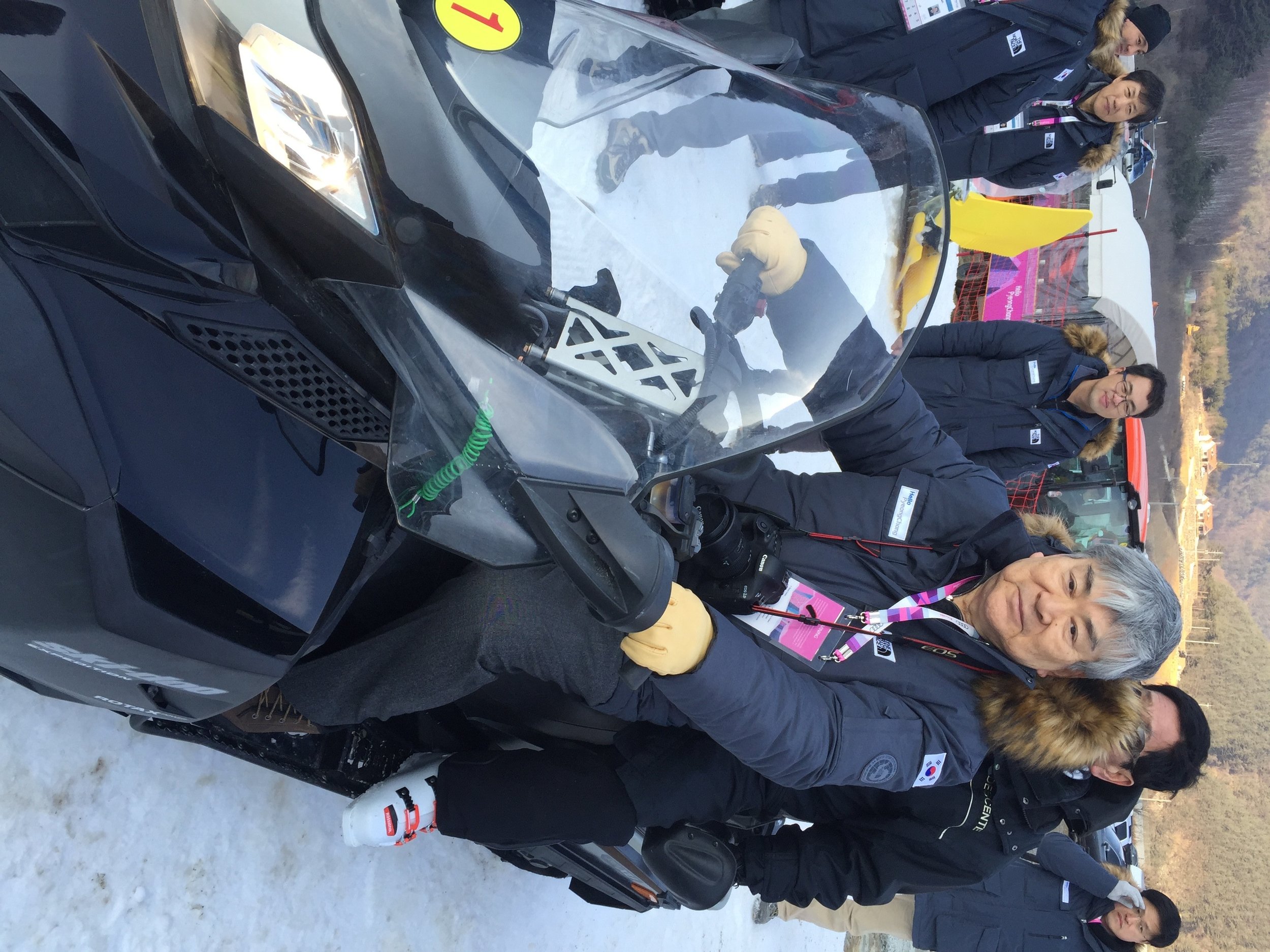
“[Garcetti] seems to have done everything in his 42 years except pitch for the Dodgers and kayak to Borneo,” adding later in the column, ”He’s George Plimpton, Bono and Seinfeld’s Mr. Peterman all rolled into one. When he says: ‘And then there was the time I commandeered a snowmobile at the North Pole while on a climate-change fact-finding mission and located Salma Hayek’s lost purse in the frozen tundra,’ he’s not kidding. He actually did that. And Hayek said he’s a great dancer.”
It was salsa dancing, for the record. And one small correction: the dancing took part in Iqaluit, the provincial capital of Nunavut, Canada.
More from Lopez on Garcetti:
"He was a cheerleader, led his Columbia U. literary society, headed a discussion group on gender and sexuality and served the homeless while composing musicals. He went on to conduct research or serve humanitarian causes in Eritrea, Ethiopia and Burma, worked for Amnesty International and became a university instructor. And did I mention that he speaks fluent Spanish and currently serves as a Naval Reserve officer?"

Larry Probst, the USOC board chair, said of Garcetti, "That guy is our secret weapon." After this week, "He's no secret anymore."
Some 1200 people were accredited for the ANOC assembly, filling a huge hall on the lower level of the Washington Hilton. Garcetti called it “breathtaking” to see such global diversity on display.
Throughout his several days here, Garcetti played it very low-key, saying repeatedly he was here to listen and learn.
After the failures of Chicago 2016 and New York 2012, it’s abundantly plain that any American bid must walk a fine line between boldness and, probably even more important, humility.
As Garcetti told Associated Press, ”People want us to be assertive and brave about the Olympic movement but not to tip over to being arrogant. It’s like, 'Win it on your merits, be a good team player. We already know how big you are, how many athletes and medals you have. Just be one of us.' "
The USOC has in recent years been oft-criticized for not playing a role commensurate with its standing — or its expected standing — in the movement. To that end, Probst said at a Wednesday night welcome gala, no fewer than 10 world championships have been or will be staged in the United States this year alone.
Upcoming: the international weightlifting championships in Houston next month. Just past: the world road cycling championships in Richmond, Virginia, which attracted 640,000 people over nine days.
The USOC, Probst said, was “delighted” to play host to the ANOC meeting, part of a plan to “become a full partner in the Olympic family and appropriately engage everywhere we thought we could make a positive difference.”
ANOC president Sheik Ahmad al-Fahad al-Sabah of Kuwait, a major Olympic power-broker, said time and again this week how important it was to gather on American soil.
At a Tuesday dinner, he said, “I just want to [emphasize] that we are back in the United States,” he said. At Wednesday’s gala, he said, referring to the Americans, “You are a main stakeholder in the Olympic movement,” adding, “Come back,” and, “You are most welcome and a big part of this family.”

A key ANOC initiative: the development and staging of the so-called Beach Games, a bid to reach out to and more actively engage with teens and 20-somethings, arguably the key demographic in the Olympic sphere. The full ANOC assembly on Friday approved the awarding of a first Beach Games, to be held in 2017, to San Diego, at a projected cost in the range of $150 million; some 20 sports are to be on the program, including surfing, volleyball and triathlon.
Just two hours, maybe less, from Los Angeles?
To avoid conflict with the IOC rule that bars members from visiting bid cities, the San Diego event is due to be held in the days after the 2024 vote.
Like that is going to stop site visits by influence-makers in the Olympic world.
What? If someone is in San Diego, are they going to be fitted with five-ringed ankle-monitors to track them from making the short drive north to LA? Are trips to Disneyland, in Orange County, halfway between San Diego and LA, off-limits?
Silly, and, again, another reason why the no-visits rule ought to be dropped, even acknowledging all IOC paranoia about sport corruption, a topic that IOC president Thomas Bach visited at length from the dais Thursday in remarks about the FIFA scandal in which he did not even once mention the acronym “FIFA.”
“Follow the news,” Bach said, adding, “Think about what it means for you: it means for you that if you do not follow these basic principles of good governance, your credibility is at risk, that the credibility of all you may have done in the past and all the good things you are doing is at risk.”
The FIFA matter, sparked by a criminal investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice, clearly poses an uncertainty for any American 2024 effort. What will the status of that matter be by September 2017? And the status of would-be systemic FIFA reconstruction?
The sheikh, who also serves on the FIFA executive committee, sought here to strike a light tone. “FIFA — we believe FIFA needs a lot of reforms,” he said at Tuesday night’s dinner to laughter.
Also a U.S. challenge: how effective can any American delegation prove at lobbying the IOC for the big prize? There are three U.S. IOC members: Probst, Anita DeFrantz, Angela Ruggiero.
USOC chief executive Scott Blackmun and Probst have worked diligently for six years at relationship-building, and Blackmun is likely to assume an ever-wider role as the bid goes on. He struck exactly the right tone at Wednesday’s gala in exceedingly brief remarks: “It’s great to have you here in the United States.”
Meanwhile, the scene at that gala, and indeed for most of the week, highlighted a significant American challenge.
It’s typical at a large-scale Olympic gathering such as an ANOC assembly for a senior federal official from the host country, typically the rank of a president or prime minister, to make -- at the least -- an appearance at which all are welcomed to wherever and wished a good time.
Russian president Vladimir Putin, for instance, opened last week's World Olympians Forum in Moscow, with Bach and Monaco's Prince Albert on hand, calling for the "de-politicization of sports under international law."
Roughly half the 100 or so IOC members were here for the ANOC proceedings -- "almost ... a quorum," as the sheikh quipped. Thus: a major opportunity.
Tuesday? Wednesday? Thursday? No senior U.S. officials.
The mayor of Washington, Muriel Bowser, offered Thursday’s welcoming remarks. Washington and San Francisco were also in the U.S. mix for 2024 along with, of course, Boston.
"As you consider future sports event, please consider Washington, D.C., a worthy option,'' Bowser said, adding later, "See you in 2028."
Talk about off-message.
President Obama, of course, made a trip to the IOC session in Copenhagen in October 2009 to pitch for Chicago, which got booted in the first round of voting. Since then, the Obama White House has played it decidedly cool with the Olympic scene.
Within the IOC, Obama is typically mentioned in discussion either with the security-related logistics of that 2009 Copenhagen visit or his decision to politicize the U.S. delegation to the 2014 Sochi Games opening ceremony as a response to the Russian law banning gay “propaganda” to minors. He selected the tennis star Billie Jean King and two other openly gay athletes for the U.S. effort. (King ultimately made it to the closing ceremony; she was unable to attend the opening ceremony because of her mother’s death.)
In just over two years as IOC president, Bach has met with roughly 100 heads of government or state. Obama? No.
On Wednesday, while ANOC delegates gathered in DC, the First Lady, Michelle Obama, and Jill Biden, the vice president's wife, met with Britain's Prince Harry in Fort Belvoir, Virginia, not far away, to promote the 2016 Invictus Games. The Paralympic-style event, to be held next May in Orlando, Florida, is intended to raise awareness for wounded service members.
“OK, ladies, Prince Harry is here. Don’t act like you don’t notice!” Mrs. Obama said, adding at another point to laughs, “I’d like to apologize for all the gold medals we will win in Orlando.” The prince said in response, “You better bring it, USA!”
Later Wednesday, the prince met President Obama in the Oval Office, again to promote the Invictus project.



So -- on Friday morning, while the Rio 2016 delegation was already in the midst of its presentation to the assembly, what was this? A surprise appearance from vice president Joe Biden, the Olympic equivalent of a protocol drive-by.
The sheikh literally had to ask producers to stop a Rio 2016 beauty video as Biden stepped up to the microphone. There, flanked by the sheikh, Bach and Probst, Biden said he'd had breakfast earlier in the week with Garcetti, who had said it was an "oversight" that "no one from the administration has been here."
"He was right," Biden said. "It was an oversight. For that, I apologize. I am a poor substitute, and I am delighted to be here." He also called the Olympics the "single unifying principle in the world.''
More Biden: "I will be the captain of the U.S. Olympic team. I'm running 100 meters. Don't I wish I could! I bet every one of you here wish you could, too."
And this: "I am not here lobbying for any city. Though I do love Los Angeles. All kidding aside, Garcetti is my friend and he won't let me back in LA unless I say something nice."
Biden closed with a note that he intended to attend the Summer Games and that when he did, "I hope when I come up to you and say, 'Hello,' you won't say, 'Joe who?' "
And then he was gone, out of the big hall.
In all, just over seven minutes.
Did Biden -- like Putin -- say anything substantive? No.
Then again, the vice-president did show up. So, ultimately, the big-picture argument can be made, Probst calling Biden's appearance "incredibly important," adding, "The message is our government at the very highest levels cares about the Olympic movement, and I hope that's a message that will resonate."
Patrick Hickey, the IOC executive board member who is also head of the European Olympic Committees, called Biden's remarks "most charming" and his appearance a "superb move," observing that "lots of people" had remarked about the prior absence of a ranking administration official.
And security? This was not Copenhagen in 2009. No disruptions. The room wasn't suddenly cleared and swept. There were no -- there have not been all week -- airport-style metal detectors.
This, then, is perhaps the ultimate take-away of this week, one likely to emerge as a key talking point for LA24 and the USOC: the United States is different. Yes, there are 206 national Olympic committees. The way stuff gets done in the U.S. can often be different than anywhere else. Not better, not worse. Just different. But, for sure, it gets done.
For emphasis: different does not mean better or worse. It's just -- different.
Come January 2017, meantime, the issue of U.S. federal involvement may prove a minor footnote in the 2024 Olympic story. That's eight months before the IOC election. That's when a new U.S. president takes office. Maybe even sooner -- whenever it will be in 2016 that the Democratic and Republican presidential nominees assume their roles.
For now, Probst said, referring to Garcetti, "We're thrilled this guy is here."